Prometheus设计
当Prometheus刮取你的实例的HTTP端点时,客户端库会将所有跟踪的指标的当前状态发送到服务器。
指标
Prometheus指标分为Counter(计数器)、Gauge(仪表盘)、Histogram(直方图)和Summary(摘要)这4类,
- Counter是计数器类型,它的特点是只增不减,例如机器启动时间、HTTP访问量等。Counter 具有很好的不相关性,不会因为机器重启而置0
- Gauge Gauge是仪表盘,表征指标的实时变化情况,可增可减,例如CPU和内存的使用量、网络 I/O 大小等,大部分监控数据都是 Gauge 类型的。
- Summary 如果需要了解某个时间段内请求的响应时间,则通常使用平均响应时间,但这样做无法体现数据的长尾效应。
- Histogram Histogram反映了某个区间内的样本个数,通过{le=”上边界”}指定这个范围内的样本数。 Prometheus中表示每个本地存储序列保存的chunk数量的指标prometheus_local_storage_series_chunks_persisted就属于Histogram指标类型
数据采集
Prometheus主要采用 Pull方式采集监控数据。
采用Push方式时,Agent主动上报数据,采用Pull方式时,监控中心(Master)拉取 Agent的数据。 为了兼容 Push方式,Prometheus 提供了 Pushgateway组件
Push方式和Pull方式进行详细对比和说明
- 实时性 Push方式的实时性相对较好,可以将采集数据立即上报到监控中心。 Pull 方式通常进行周期性采集,采集时间为30s 或者更长时间。 如果对监控系统的实时性要求非常高,则建议采用Push方式。
- 状态保存 Push 方式通常在采集完成后立即上报,本地不会保存采集数据,Agent 本身是没有状态的,而Master需要维护各种Agent状态。 Pull 方式正好相反,Agent 本身需要有一定的数据存储能力,Master 只负责简单的数据拉取,而且Master本身可以做到无状态。
- 控制能力 采用Push方式时,控制方为Agent,Agent上报的数据决定了上报的周期和内容。 采用Pull方式时,Master更加主动,控制采集的内容和频率。
- 配置的复杂性 采用Push方式时,通常每个 Agent都需要配置Master的地址。采用Pull方式时,通常通过批量配置或者自动发现来获取所有采集点。
服务发现
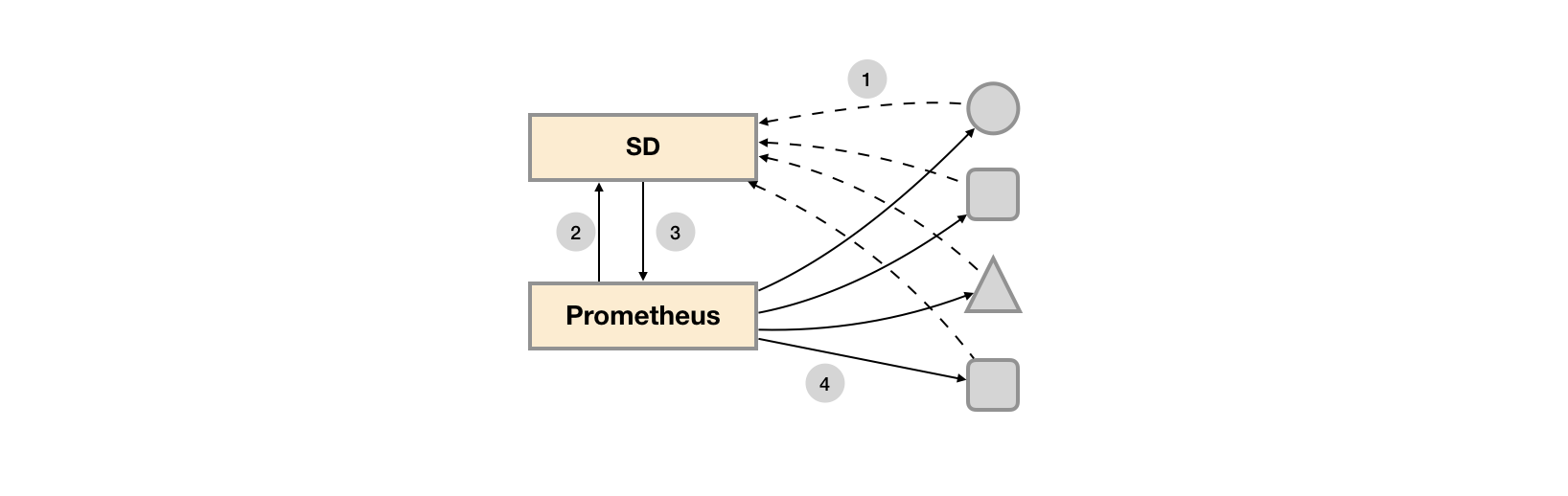 在基于云(IaaS或者CaaS)的基础设施环境中用户可以像使用水、电一样按需使用各种资源(计算、网络、存储)。按需使用就意味着资源的动态性,这些资源可以随着需求规模的变化而变化。
在基于云(IaaS或者CaaS)的基础设施环境中用户可以像使用水、电一样按需使用各种资源(计算、网络、存储)。按需使用就意味着资源的动态性,这些资源可以随着需求规模的变化而变化。
对于Prometheus这一类基于Pull模式的监控系统,显然也无法继续使用的static_configs的方式静态的定义监控目标。
Prometheus 获取被采集的对象,有两种方式:静态文件配置和动态发现。
- 静态文件配置 静态文件配置是一种传统的服务发现方式,一般适用于有固定的监控环境、IP地址和统一的服务接口的场景,需要在配置中指定采集的目标。
- 动态发现
动态发现方式比较适合在云环境下使用。云的理念就是按需供给,资源是动态分配的,并且生命周期比物理机器短。
◎ 动态伸缩场景
◎ 迅速配置场景
Prometheus动态发现方式获取监控对象。目前支持以下系统获取监控对象:
◎ 容器管理系统,例如Kubernetes、Marathon;
◎ 各种云管平台,例如EC2、Azure、OpenStack;
◎ 各种服务发现组件,例如DNS、ZooKeeper和Consul等。

实现细节参考:https://yunlzheng.gitbook.io/prometheus-book/part-ii-prometheus-jin-jie/sd
数据查询
Prometheus实现了一套自己的数据库语言(PromQL)解析器
Prometheus支持Grafana等开源显示面板,通过自定义PromQL可以制作丰富的监控视图。Prometheus本身也提供了一个简单的 Web查询控制台,如图2-14所示,Web控制台包含三个主要模块:Graph指标查询,Alerts告警查询、Status状态查询
正则匹配
-
使用
=~进行正则表达式匹配:http_requests_total{job=~"job[12]"}上述查询会匹配包含
job1或job2的指标。 -
使用
!=进行不匹配操作:http_requests_total{job!="job1"}上述查询会匹配不包含
job1的指标。 -
使用
:re函数进行正则表达式匹配:http_requests_total{job:re="job[12]"}上述查询同样会匹配包含
job1或job2的指标。 -
使用
=~进行标签名的正则表达式匹配:{__name__=~"job.*"}上述查询会匹配指标名称以
job开头的所有指标。
{__name__=~".*job.*"}
查询会匹配指标名称包含 job 的所有指标。
这些是一些常见的 PromQL 模糊匹配操作。使用这些操作可以灵活地对指标进行匹配和过滤。根据实际需求,可以结合不同的匹配方式来查询所需的指标数据。
语法
# 指定默认值
sum(your_query) or vector(1)
go demo
package main
import (
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus/promauto"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/prometheus/promhttp"
)
func recordMetrics() {
go func() {
for {
opsProcessed.Inc()
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
}
}()
}
var (
opsProcessed = promauto.NewCounter(prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "myapp_processed_ops_total",
Help: "The total number of processed events",
})
)
func main() {
recordMetrics()
http.Handle("/management/metrics", promhttp.Handler())
http.ListenAndServe(":2112", nil)
}
// Counter applications:
// 1、static success nums;
// 2、static fail nums;
// 3、static event nums;
// metrics format:
查看写入指标 http://localhost:2112/management/metrics
采集对象
Kubernetes资源相关
- CPUThrottlingHigh
关于 CPU 的 limit 合理性指标。查出最近5分钟,超过25%的 CPU 执行周期受到限制的容器。表达式:
sum(increase(container_cpu_cfs_throttled_periods_total{container!="", }[5m])) by (container, pod, namespace) / sum(increase(container_cpu_cfs_periods_total{}[5m])) by (container, pod, namespace) > ( 25 / 100 )相关指标:
- container_cpu_cfs_periods_total:容器生命周期中度过的 cpu 周期总数
- container_cpu_cfs_throttled_periods_total:容器生命周期中度过的受限的 cpu 周期总数
- histogram_quantile
根据传统直方图或原生直方图计算 φ 分位数 (0 ≤ φ ≤ 1)
-- 计算过去 10 分钟内请求持续时间的第 90 个百分位数 histogram_quantile(0.9, rate(http_request_duration_seconds_bucket[10m]))
Promethues Histograms是测量PRC延迟分布的好方法
- grpc_server_handling_seconds_bucket - 包含在各个处理时间桶中按状态和方法计算的RPC计数。 Prometheus可以使用这些桶来估计SLA(见这里) 应用 ```sql – Latency P99,计算时间范围内服务99%接口的延迟分布 – le 延迟时间 histogram_quantile(0.99, sum(irate(grpc_server_handling_seconds_bucket{grpc_service=”qimao.bigdata.data.Gateway”}[$interval])) by (grpc_method,le)
)
- offset 指定偏移量
rate(http_requests_total[5m] offset -1w)
https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/querying/basics/
参考:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1667912
## debug
profiling https://training.promlabs.com/training/monitoring-and-debugging-prometheus/profiling
### pprof
Prometheus 服务器,与大多数用 Go 编写的严格的软件一样,使用标准库中名为 pprof 的包进行检测,该包使用特定格式提供运行时分析信息。
以这种格式生成的文件随后可以由具有相同名称 (pprof) 的命令行工具读取,该工具使用它们生成分析数据的报告和可视化。 promtool 提供了 debug pprof 子命令,我们可以在以下代码片段中看到它的运行情况:
```shell
~$ promtool debug pprof 'http://prometheus:9090'
****collecting: http://prometheus:9090/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=30****collecting: http://prometheus:9090/debug/pprof/block****collecting: http://prometheus:9090/debug/pprof/goroutine****collecting: http://prometheus:9090/debug/pprof/heap ...**
可以使用web方式查看cpu情况,执行命令:
go tool pprof -http=:6060 http://prometheus:9090/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=30
文档说明: https://training.promlabs.com/training/monitoring-and-debugging-prometheus/profiling/profiling-cpu-usage
参考
正则查询: https://prometheus.fuckcloudnative.io/di-san-zhang-prometheus/di-4-jie-cha-xun/basics
go-application https://prometheus.io/docs/guides/go-application/
服务发现 https://yunlzheng.gitbook.io/prometheus-book/part-ii-prometheus-jin-jie/sd/why-need-service-discovery